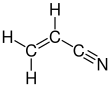
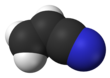
Acrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile
| | |||
| | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Prop-2-enenitrile | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.152 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1093 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H3N | |||
| Molar mass | 53.064 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.81 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −84 °C (−119 °F; 189 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 77 °C (171 °F; 350 K) | ||
| 70 g/L | |||
| log P | 0.19[2] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 83 mmHg[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | flammable reactive toxic potential occupational carcinogen[1] | ||
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 0092 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −1 °C; 30 °F; 272 K | ||
| 471 °C (880 °F; 744 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 3–17% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration) | 500 ppm (rat, 4 h) 313 ppm (mouse, 4 h) 425 ppm (rat, 4 h)[3] | ||
LCLo (lowest published) | 260 ppm (rabbit, 4 h) 575 ppm (guinea pig, 4 h) 636 ppm (rat, 4 h) 452 ppm (human, 1 h)[3] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) | TWA 2 ppm C 10 ppm [15-minute] [skin][1] | ||
REL (Recommended) | Ca TWA 1 ppm C 10 ppm [15-minute] [skin][1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) | 85 ppm[1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related nitriles | acetonitrile propionitrile | ||
Related compounds | acrylic acid acrolein | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Acrylonitrile is an organic compound with the formula CH2CHCN. It is a colorless volatile liquid although commercial samples can be yellow due to impurities. It has a pungent odor of garlic or onions.[4] In terms of its molecular structure, it consists of a vinyl group linked to a nitrile. It is an important monomer for the manufacture of useful plastics such as polyacrylonitrile. It is reactive and toxic at low doses.[5] Acrylonitrile was first synthesized by the French chemist Charles Moureu (1863–1929) in 1893.[6]
Occurrence[edit]
Acrylonitrile is not naturally formed in the atmosphere of Earth. However it can occur at levels up to 0.11 ppm at industrial sites. It persists in the air for up to a week. It decomposes by reacting with oxygen and hydroxyl radical to form formyl cyanide and formaldehyde.[7] Acrylonitrile is harmful to aquatic life.[8]
Acrylonitrile has been detected in the atmosphere of Titan, a moon of Saturn.[9][10][11] Computer simulations suggest that on Titan conditions exist such that the compound could form structures similar to cell membranes and vesicles on Earth.[9][10]
Production[edit]
Acrylonitrile is produced by catalytic ammoxidation of propylene, also known as the SOHIO process. In 2002, world production capacity was estimated at 5 million tonnes per year.[5][12] Acetonitrile and hydrogen cyanide are significant byproducts that are recovered for sale.[5] In fact, the 2008–2009 acetonitrile shortage was caused by a decrease in demand for acrylonitrile.[13]
In the SOHIO process, propylene, ammonia, and air (oxidizer) are passed through a fluidized bed reactor containing the catalyst at 400–510 °C and 50–200 kPag. The reactants pass through the reactor only once, before being quenched in aqueous sulfuric acid. Excess propylene, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and dinitrogen that do not dissolve are vented directly to the atmosphere, or are incinerated. The aqueous solution consists of acrylonitrile, acetonitrile, hydrocyanic acid, and ammonium sulfate (from excess ammonia). A recovery column removes bulk water, and acrylonitrile and acetonitrile are separated by distillation. Historically, one of the first successful catalysts was bismuth phosphomolybdate (Bi9PMo12O52) supported on silica as a heterogeneous catalyst.[14] Further improvements have since been made.[5]
Emerging industrial routes[edit]
Various green chemistry routes are being developed for the synthesis of acrylonitrile from renewable feedstocks, such as lignocellulosic biomass, glycerol (from biodiesel production), or glutamic acid (which can itself be produced from renewable feedstocks). The lignocellulosic route involves fermentation of the biomass to propionic acid and 3-hydroxypropionic acid which are then converted to acrylonitrile by dehydration and ammoxidation.[15] The glycerol route begins with pyrolysis to acrolein, which undergoes ammoxidation to give acrylonitrile.[16] The glutamic acid route employs oxidative decarboxylation to 3-cyanopropanoic acid, followed by a decarbonylation-elimination to acrylonitrile.[17] Of these, the glycerol route is broadly considered to be the most viable, although current methods are still unable to compete with the SOHIO process in terms of cost.[15][16]
Uses[edit]
Acrylonitrile is used principally as a monomer to prepare polyacrylonitrile, a homopolymer, or several important copolymers, such as styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA), and other synthetic rubbers such as acrylonitrile butadiene (NBR). Hydrodimerization of acrylonitrile affords adiponitrile, used in the synthesis of certain nylons:
- 2 CH2=CHCN + 2 e− + 2 H+ → NCCH2CH2CH2CH2CN
Small amounts are also used as a fumigant. Acrylonitrile and derivatives, such as 2-chloroacrylonitrile, are dienophiles in Diels–Alder reactions. Acrylonitrile is also a precursor in the industrial manufacture of acrylamide and acrylic acid.[5]
Health effects[edit]
Acrylonitrile is highly flammable and toxic at low doses. It undergoes explosive polymerization. The burning material releases fumes of hydrogen cyanide and oxides of nitrogen. It is classified as a Class 2B carcinogen (possibly carcinogenic) by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC),[18] and workers exposed to high levels of airborne acrylonitrile are diagnosed more frequently with lung cancer than the rest of the population.[19] Acrylonitrile increases cancer in high dose tests in male and female rats and mice[20] and induces apoptosis in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.[21]
It evaporates quickly at room temperature (20 °C) to reach dangerous concentrations; skin irritation, respiratory irritation, and eye irritation are the immediate effects of this exposure.[8] Pathways of exposure for humans include emissions, auto exhaust, and cigarette smoke that can expose the human subject directly if they inhale or smoke. Routes of exposure include inhalation, oral, and to a certain extent dermal uptake (tested with volunteer humans and in rat studies).[22] Repeated exposure causes skin sensitization and may cause central nervous system and liver damage.[8]
There are two main excretion processes of acrylonitrile. The primary method is excretion in urine when acrylonitrile is metabolized by being directly conjugated to glutathione. The other method is when acrylonitrile is enzymatically converted into 2-cyanoethylene oxide which will produce cyanide end products that ultimately form thiocyanate, which is excreted via urine.[22] Exposure can this be detected via blood draws and urine sampling.[18]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0014". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Acrylonitrile_msds".
- ^ a b "Acrylonitrile". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Medical Management Guidelines for Acrylonitrile". Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry. Retrieved 2020-06-10.
- ^ a b c d e Brazdil, James F. "Acrylonitrile". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_177.pub3.
- ^
- Moureu, C. (1893). "Contribution à l'étude de l'acide acrylique et de ses dérivés" [Contribution to the study of acrylic acid and of its derivatives]. Annales de chimie et de physique. 7th. 2: 145–212. See especially pp. 187–189 ("Nitrile acrylique ou cyanure de vinyle (Propène-nitrile)").
- Moureu, C. (1893). "Nitrile acrylique, cyanure de vinyle (propène-nitrile)" [Acrylic nitrile, vinyl cyanide (propenenitrile)]. Bulletin de la Société Chimique de France. 3rd. 9: 424–427.
- ^ Grosjean, Daniel (December 1990). "Atmospheric Chemistry of Toxic Contaminants. 3. Unsaturated Aliphatics: Acrolein, Acrylonitrile, Maleic Anhydride". Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association. 40 (12): 1664–1669. doi:10.1080/10473289.1990.10466814.
- ^ a b c "CDC – Acrylonitrile – International Chemical Safety Cards". www.cdc.gov. NIOSH. Retrieved 2015-07-31.
- ^ a b Wall, Mike (28 July 2017). "Saturn Moon Titan Has Molecules That Could Help Make Cell Membranes". Space.com. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ^ a b Palmer, Maureen Y.; et al. (28 July 2017). "ALMA detection and astrobiological potential of vinyl cyanide on Titan". Science Advances. 3 (7): e1700022. Bibcode:2017SciA....3E0022P. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1700022. PMC 5533535. PMID 28782019.
- ^ Kaplan, Sarah (8 August 2017). "This weird moon of Saturn has some essential ingredients for life". The Washington Post. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- ^ "The Sohio Acrylonitrile Process". American Chemical Society National Historic Chemical Landmarks. Archived from the original on 2013-02-23. Retrieved 2013-05-13.
- ^ Tullo, A. (2008). "A Solvent Dries Up". Chemical & Engineering News. 86 (47): 27. doi:10.1021/cen-v086n047.p027.
- ^ Grasselli, Robert K. (2014). "Site isolation and phase cooperation: Two important concepts in selective oxidation catalysis: A retrospective". Catalysis Today. 238: 10–27. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2014.05.036.
- ^ a b Grasselli, Robert K.; Trifirò, Ferruccio (2016). "Acrylonitrile from Biomass: Still Far from Being a Sustainable Process". Topics in Catalysis. 59 (17–18): 1651–1658. doi:10.1007/s11244-016-0679-7. ISSN 1022-5528. S2CID 99550463.
- ^ a b Guerrero-Pérez, M. Olga; Bañares, Miguel A. (2015). "Metrics of acrylonitrile: From biomass vs. petrochemical route". Catalysis Today. 239: 25–30. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2013.12.046. ISSN 0920-5861.
- ^ Le Nôtre, Jérôme; Scott, Elinor L.; Franssen, Maurice C. R.; Sanders, Johan P. M. (2011). "Biobased synthesis of acrylonitrile from glutamic acid". Green Chemistry. 13 (4): 807. doi:10.1039/c0gc00805b. ISSN 1463-9262.
- ^ a b "Re-evaluation of Some Organic Chemicals, Hydrazine and Hydrogen Peroxide". IARC Monographs, Volume 71 (1999)
- ^ Acrylonitrile Fact Sheet (CAS No. 107-13-1). epa.gov
- ^ "Acrylonitrile: Carcinogenic Potency Database".
- ^ Sun, X. (January 2014). "Cytotoxic effects of acrylonitrile on human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro". Molecular Medicine Reports. 9 (1): 97–102. doi:10.3892/mmr.2013.1802. PMID 24248151.
- ^ a b Acrylonitrile Fact Sheet: Support Document (CAS No. 107-13-1). epa.gov
External links[edit]
- National Pollutant Inventory – Acrylonitrile
- Comparing Possible Cancer Hazards from Human Exposures to Rodent Carcinogens
- Acrylonitrile – Integrated Risk Information System, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
- CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Acrylonitrile
- OSHA Table Z-1 for Air Contaminants




Comments
Post a Comment